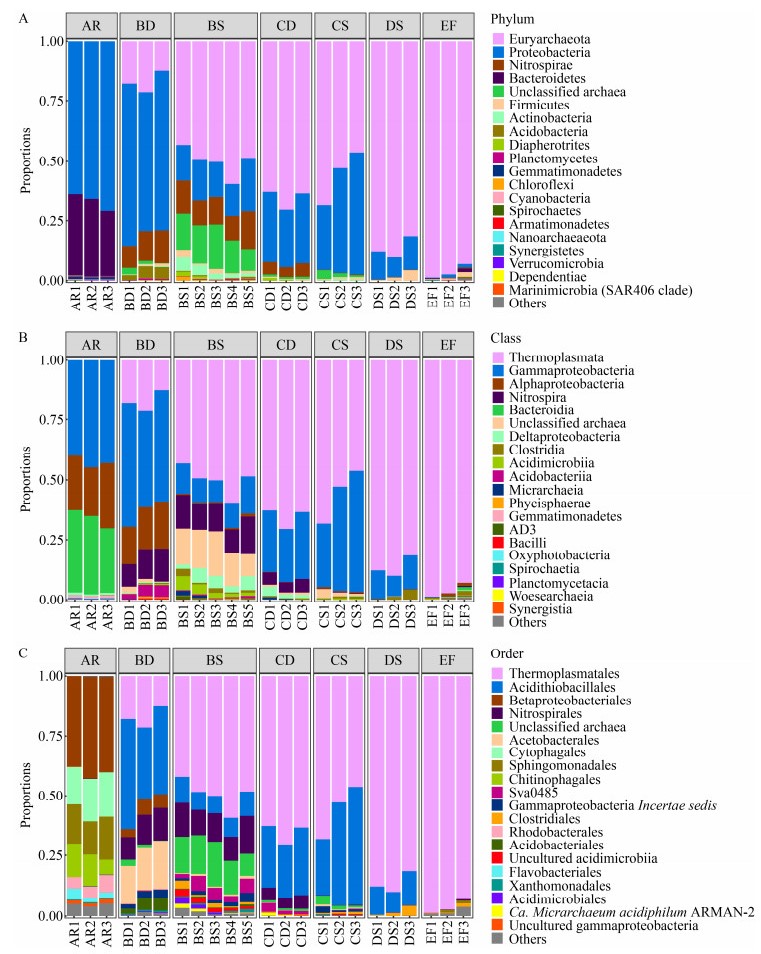
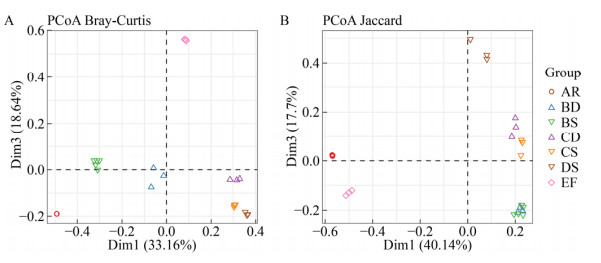
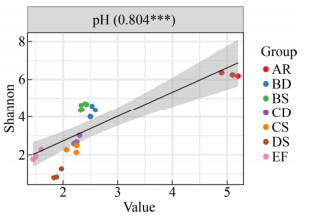
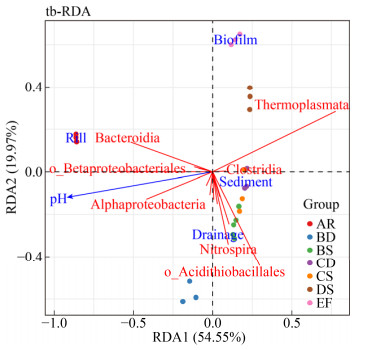
| [1] | |
|
| [2] | |
|
| [3] |
Kefeni KK, Msagati TAM, Mamba BB. Acid mine drainage: prevention, treatment options, and resource recovery: a review. J Clean Prod, 2017, 151: 475-493. DOI:10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.03.082 |
|
| [4] | |
|
| [5] |
Evangelou VP, Zhang YL. A review: pyrite oxidation mechanisms and acid mine drainage prevention. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol, 1995, 25(2): 141-199. DOI:10.1080/10643389509388477 |
|
| [6] | |
|
| [7] | |
|
| [8] | |
|
| [9] | |
|
| [10] |
Bonnefoy V, Holmes DS. Genomic insights into microbial iron oxidation and iron uptake strategies in extremely acidic environments. Environ Microbiol, 2012, 14(7): 1597-1611. DOI:10.1111/j.1462-2920.2011.02626.x |
|
| [11] |
Dopson M, Johnson DB. Biodiversity, metabolism and applications of acidophilic sulfur-metabolizing microorganisms. Environ Microbiol, 2012, 14(10): 2620-2631. DOI:10.1111/j.1462-2920.2012.02749.x |
|
| [12] |
Bond PL, Druschel GK, Banfield JF. Comparison of acid mine drainage microbial communities in physically and geochemically distinct ecosystems. Appl Environ Microbiol, 2000, 66(11): 4962-4971. DOI:10.1128/AEM.66.11.4962-4971.2000 |
|
| [13] |
Méndez-García C, Mesa V, Sprenger RR, et al. Microbial stratification in low pH oxic and suboxic macroscopic growths along an acid mine drainage. ISME J, 2014, 8(6): 1259-1274. DOI:10.1038/ismej.2013.242 |
|
| [14] |
Chen LX, Hu M, Huang LN, et al. Comparative metagenomic and metatranscriptomic analyses of microbial communities in acid mine drainage. ISME J, 2015, 9(7): 1579-1592. DOI:10.1038/ismej.2014.245 |
|
| [15] | |
|
| [16] |
Kuang JL, Huang LN, He ZL, et al. Predicting taxonomic and functional structure of microbial communities in acid mine drainage. ISME J, 2016, 10(6): 1527-1539. DOI:10.1038/ismej.2015.201 |
|
| [17] |
Chen LX, Huang LN, Méndez-García C, et al. Microbial communities, processes and functions in acid mine drainage ecosystems. Curr Opin Biotechnol, 2016, 38: 150-158. DOI:10.1016/j.copbio.2016.01.013 |
|
| [18] | |
|
| [19] |
Rawlings DE, Johnson DB. The microbiology of biomining: development and optimization of mineral-oxidizing microbial consortia. Microbiology, 2007, 153(2): 315-324. DOI:10.1099/mic.0.2006/001206-0 |
|
| [20] |
Li KW, Zhang Q, Wang DP, et al. Isotope geochemistry of Bainiuchang silver polymetallic deposits in Mengzi, Yunnan. Mineral Deposits, 2010, 29(S1): 462-463 (in Chinese). 李开文, 张乾, 王大鹏, 等. 云南蒙自白牛厂银多金属矿床同位素地球化学研究. 矿床地质, 2010, 29(S1): 462-463. |
|
| [21] | |
|
| [22] |
Kuang JL, Huang LN, Chen LX, et al. Contemporary environmental variation determines microbial diversity patterns in acid mine drainage. ISME J, 2013, 7(5): 1038-1050. DOI:10.1038/ismej.2012.139 |
|
| [23] | |
|
| [24] | |
|
| [25] |
Martin M. Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnet J, 2011, 17(1): 3. DOI:10.14806/ej.17.1.202 |
|
| [26] |
Edgar RC. UPARSE: highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat Methods, 2013, 10(10): 996-998. DOI:10.1038/nmeth.2604 |
|
| [27] |
Edgar RC. UNOISE2: improved error-correction for Illumina 16S and ITS amplicon sequencing. BioRxiv, 2016, 081257. |
|
| [28] |
Bolyen E, Rideout JR, Dillon MR, et al. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QⅡME 2. Nat Biotechnol, 2019, 37(8): 852-857. DOI:10.1038/s41587-019-0209-9 |
|
| [29] |
Wang Q, Garrity GM, Tiedje JM, et al. Naive Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl Environ Microbiol, 2007, 73(16): 5261-5267. DOI:10.1128/AEM.00062-07 |
|
| [30] |
Korzhenkov AA, Toshchakov SV, Bargiela R, et al. Archaea dominate the microbial community in an ecosystem with low-to-moderate temperature and extreme acidity. Microbiome, 2019, 7: 11. DOI:10.1186/s40168-019-0623-8 |
|
| [31] | |
|
| [32] |
Tan S, Liu J, Fang Y, et al. Insights into ecological role of a new deltaproteobacterial order Candidatus Acidulodesulfobacterales by metagenomics and metatranscriptomics. ISME J, 2019, 13(8): 2044-2057. DOI:10.1038/s41396-019-0415-y |
|
| [33] |
Yelton AP, Comolli LR, Justice NB, et al. Comparative genomics in acid mine drainage biofilm communities reveals metabolic and structural differentiation of co-occurring archaea. BMC Genomics, 2013, 14: 485. DOI:10.1186/1471-2164-14-485 |
|
| [34] |
Cao ZM, Banda JF, Pei LX, et al. Microbial community structure characteristics in different mine drainage lakes of an iron mine in Anhui Province. Acta Microbiol Sin, 2019, 59(6): 1076-1088 (in Chinese). 曹子敏, Banda JF, 裴理鑫, 等. 安徽某铁矿不同矿山废水库中微生物群落结构特征. 微生物学报, 2019, 59(6): 1076-1088. |
|
| [35] | |
|
| [36] |
Yeoh YK, Sekiguchi Y, Parks DH, et al. Comparative genomics of candidate phylum TM6 suggests that parasitism is widespread and ancestral in this lineage. Mol Biol Evol, 2016, 33(4): 915-927. DOI:10.1093/molbev/msv281 |
|
| [37] |
Mesa V, Gallego JLR, González-Gil R, et al. Bacterial, archaeal, and eukaryotic diversity across distinct microhabitats in an acid mine drainage. Front Microbiol, 2017, 8: 1756. DOI:10.3389/fmicb.2017.01756 |
|
| [38] |
Amaral-Zettler LA, Zettler ER, Theroux SM, et al. Microbial community structure across the tree of life in the extreme Río Tinto. ISME J, 2011, 5(1): 42-50. DOI:10.1038/ismej.2010.101 |
|
| [39] |
Gavrilov SN, Korzhenkov AA, Kublanov IV, et al. Microbial communities of polymetallic deposits' acidic ecosystems of continental climatic zone with high temperature contrasts. Front Microbiol, 2019, 10: 1573. DOI:10.3389/fmicb.2019.01573 |
|
| [40] |
Johnson DB, Hallberg KB, Hedrich S. Uncovering a microbial enigma: isolation and characterization of the streamer-generating, iron-oxidizing, acidophilic bacterium " Ferrovum myxofaciens". Appl Environ Microbiol, 2014, 80(2): 672-680. DOI:10.1128/AEM.03230-13 |
|
| [41] |
Hua ZS, Han YJ, Chen LX, et al. Ecological roles of dominant and rare prokaryotes in acid mine drainage revealed by metagenomics and metatranscriptomics. ISME J, 2015, 9(6): 1280-1294. DOI:10.1038/ismej.2014.212 |
|
| [42] |
Hallberg KB, Coupland K, Kimura S, et al. Macroscopic streamer growths in acidic, metal-rich mine waters in north wales consist of novel and remarkably simple bacterial communities. Appl Environ Microbiol, 2006, 72(3): 2022-2030. DOI:10.1128/AEM.72.3.2022-2030.2006 |
|
| [43] |
Falagán C, Moya-Beltrán A, Castro M, et al. Acidithiobacillus sulfuriphilus sp. nov.: an extremely acidophilic sulfur-oxidizing chemolithotroph isolated from a neutral pH environment. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol, 2019, 69(9): 2907-2913. DOI:10.1099/ijsem.0.003576 |
|
| [44] |
Schrenk MO, Edwards KJ, Goodman RM, et al. Distribution of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans and Leptospirillum ferrooxidans: implications for generation of acid mine drainage. Science, 1998, 279(5356): 1519-1522. DOI:10.1126/science.279.5356.1519 |
|
| [45] |
Golyshina OV, Timmis KN. Ferroplasma and relatives, recently discovered cell wall-lacking archaea making a living in extremely acid, heavy metal-rich environments. Environ Microbiol, 2005, 7(9): 1277-1288. DOI:10.1111/j.1462-2920.2005.00861.x |
|
| [46] |
Golyshina OV, Pivovarova TA, Karavaiko GI, et al. Ferroplasma acidiphilum gen. nov., sp. nov., an acidophilic, autotrophic, ferrous-iron-oxidizing, cell-wall-lacking, mesophilic member of the Ferroplasmaceae fam. nov., comprising a distinct lineage of the Archaea. nt J Syst Evol Microbiol, 2000, 50(3): 997-1006. DOI:10.1099/00207713-50-3-997 |
|
| [47] |
Dopson M, Baker-Austin C, Hind A, et al. Characterization of Ferroplasma isolates and Ferroplasma acidarmanus sp. nov., extreme acidophiles from acid mine drainage and industrial bioleaching environments. Appl Environ Microbiol, 2004, 70(4): 2079-2088. DOI:10.1128/AEM.70.4.2079-2088.2004 |
|
| [48] |
Edwards KJ, Bond PL, Gihring TM, et al. An archaeal iron-oxidizing extreme acidophile important in acid mine drainage. Science, 2000, 287(5459): 1796-1799. DOI:10.1126/science.287.5459.1796 |
|
| [49] |
Hiraishi A, Nagashima KV, Matsuura K, et al. Phylogeny and photosynthetic features of Thiobacillus acidophilus and related acidophilic bacteria: its transfer to the genus Acidiphilium as Acidiphilium acidophilum comb. nov. Int J Syst Bacteriol, 1998, 48(4): 1389-1398. DOI:10.1099/00207713-48-4-1389 |
|
| [50] |
Johnson DB, Bacelar-Nicolau P, Okibe N, et al. Ferrimicrobium acidiphilum gen. nov., sp. nov. and Ferrithrix thermotolerans gen. nov., sp. nov.: heterotrophic, iron-oxidizing, extremely acidophilic actinobacteria. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol, 2009, 59(5): 1082-1089. DOI:10.1099/ijs.0.65409-0 |
|
| [51] |
Falagán C, Johnson DB. Acidibacter ferrireducens gen. nov., sp. nov.: an acidophilic ferric iron-reducing gammaproteobacterium. Extremophiles, 2014, 18(6): 1067-1073.
|
|
| [52] |
Küsel K, Dorsch T, Acker G, et al. Microbial reduction of Fe(Ⅲ) in acidic sediments: Isolation of Acidiphilium cryptum JF-5 capable of coupling the reduction of Fe(Ⅲ) to the oxidation of glucose. Appl Environ Microbiol, 1999, 65(8): 3633-3640. |
|
| [53] | |
|
| [54] |
Falagan C, Foesel B, Johnson B. Acidicapsa ferrireducens sp. nov., Acidicapsa acidiphila sp. nov., and Granulicella acidiphila sp. nov.: novel acidobacteria isolated from metal-rich acidic waters. Extremophiles, 2017, 21(3): 459-469. DOI:10.1007/s00792-017-0916-4 |
|
| [55] | |
|
| [56] |
Johnson DB, Joulian C, d'Hugues P, et al. Sulfobacillus benefaciens sp. nov., an acidophilic facultative anaerobic Firmicute isolated from mineral bioleaching operations. Extremophiles, 2008, 12(6): 789-798. DOI:10.1007/s00792-008-0184-4 |
|
| [57] |
Druschel GK, Baker BJ, Gihring TM, et al. Acid mine drainage biogeochemistry at Iron Mountain, California. Geochem Trans, 2004, 5: 13. DOI:10.1186/1467-4866-5-13 |
|
 2019, Vol. 35
2019, Vol. 35