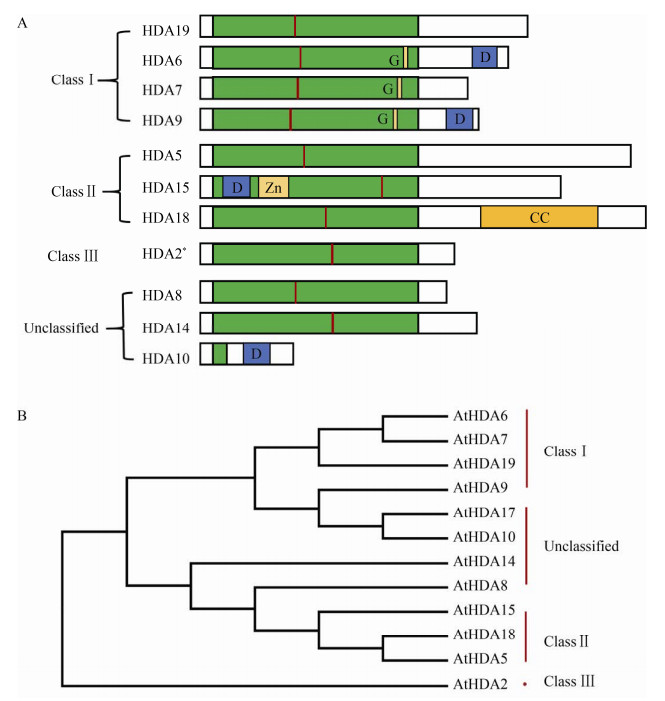
| [1] | |
|
| [2] | |
|
| [3] | |
|
| [4] |
Su YH, Wang SL, Zhang F, et al. Phosphorylation of histone H2A at serine 95: a plant-specific mark involved in flowering time regulation and H2A.Z deposition. Plant Cell, 2017, 29(9): 2197-2213. DOI:10.1105/tpc.17.00266
|
|
| [5] |
Lin G, Zhou Y, Li M, et al. Histone 3 lysine 36 to methionine mutations stably interact with and sequester SDG8 in Arabidopsis thaliana. Sci China Life Sci, 2018, 61(2): 225-234. DOI:10.1007/s11427-017-9162-1
|
|
| [6] |
Qian SM, Lv XC, Scheid RN, et al. Dual recognition of H3K4me3 and H3K27me3 by a plant histone reader SHL. Nat Commun, 2018, 9: 2425. DOI:10.1038/s41467-018-04836-y
|
|
| [7] |
Yang ZL, Qian SM, Scheid RN, et al. EBS is a bivalent histone reader that regulates floral phase transition in Arabidopsis. Nature Genet, 2018, 50: 1247-1253. DOI:10.1038/s41588-018-0187-8
|
|
| [8] |
Liu R, Li XQ, Chen W, et al. Structure and mechanism of plant histone mark readers. Sci China Life Sci, 2018, 61(2): 170-177. DOI:10.1007/s11427-017-9163-4
|
|
| [9] |
Grunstein M. Histone acetylation in chromatin structure and transcription. Nature, 1997, 389(6649): 349-352. DOI:10.1038/38664
|
|
| [10] |
Struhl K. Histone acetylation and transcriptional regulatory mechanisms. Genes Dev, 1998, 12(5): 599-606. DOI:10.1101/gad.12.5.599
|
|
| [11] | |
|
| [12] |
Lusser A, Brosch G, Loidl A, et al. Identification of maize histone deacetylase HD2 as an acidic nucleolar phosphoprotein. Science, 1997, 277(5322): 88-91. DOI:10.1126/science.277.5322.88
|
|
| [13] |
Dangl M, Brosch G, Haas H, et al. Comparative analysis of HD2 type histone deacetylases in higher plants. Planta, 2001, 213(2): 280-285. DOI:10.1007/s004250000506
|
|
| [14] |
Wu KQ, Tian LN, Malik K, et al. Functional analysis of HD2 histone deacetylase homologues in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J, 2000, 22(1): 19-27. DOI:10.1046/j.1365-313x.2000.00711.x
|
|
| [15] |
Frye RA. Phylogenetic classification of prokaryotic and eukaryotic Sir2-like proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2000, 273(2): 793-798. DOI:10.1006/bbrc.2000.3000
|
|
| [16] |
Pandey R, Müller A, Napoli CA, et al. Analysis of histone acetyltransferase and histone deacetylase families of Arabidopsis thaliana suggests functional diversification of chromatin modification among multicellular eukaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res, 2002, 30(23): 5036-5055. DOI:10.1093/nar/gkf660
|
|
| [17] |
Cigliano RA, Cremona G, Paparo R, et al. Histone deacetylase AtHDA7 is required for female gametophyte and embryo development in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol, 2013, 163(1): 431-440. DOI:10.1104/pp.113.221713
|
|
| [18] |
Tran HT, Nimick M, Uhrig RG, et al. Arabidopsis thaliana histone deacetylase 14 (HDA14) is an α-tubulin deacetylase that associates with PP2A and enriches in the microtubule fraction with the putative histone acetyltransferase ELP3. Plant J, 2012, 71(2): 263-272. DOI:10.1111/j.1365-313X.2012.04984.x
|
|
| [19] |
Liu C, Li LC, Chen WQ, et al. HDA18 affects cell fate in Arabidopsis root epidermis via histone acetylation at four kinase genes. Plant Cell, 2013, 25(1): 257-269. DOI:10.1105/tpc.112.107045
|
|
| [20] |
Wu KQ, Zhang L, Zhou CH, et al. HDA6 is required for jasmonate response, senescence and flowering in Arabidopsis. J Exp Bot, 2008, 59(2): 225-234. DOI:10.1093/jxb/erm300
|
|
| [21] |
Yu CW, Liu XC, Luo M, et al. HISTONE DEACETYLASE 6 interacts with FLOWERING LOCUS D and regulates flowering in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol, 2011, 156(1): 173-184. DOI:10.1104/pp.111.174417
|
|
| [22] |
He YH, Michaels SD, Amasino RM. Regulation of flowering time by histone acetylation in Arabidopsis. Science, 2003, 302(5651): 1751-1754. DOI:10.1126/science.1091109
|
|
| [23] |
Jiang DH, Yang WN, He YH, et al. Arabidopsis relatives of the human lysine-specific demethylase 1 repress the expression of FWA and FLOWERING LOCUS C and thus promote the floral transition. Plant Cell, 2007, 19(10): 2975-2987. DOI:10.1105/tpc.107.052373
|
|
| [24] |
Luo M, Tai R, Yu CW, et al. Regulation of flowering time by the histone deacetylase HDA5 in Arabidopsis. Plant J, 2015, 82(6): 925-936. DOI:10.1111/tpj.12868
|
|
| [25] |
Stevenson-Paulik J, Odom AR, York JD. Molecular and biochemical characterization of two plant inositol polyphosphate 6-/3-/5-kinases. J Biol Chem, 2002, 277(45): 42711-42718. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M209112200
|
|
| [26] |
Xia HJ, Brearley C, Elge S, et al. Arabidopsis inositol polyphosphate 6-/3-kinase is a nuclear protein that complements a yeast mutant lacking a functional ArgR-Mcm1 transcription complex. Plant Cell, 2003, 15(2): 449-463. DOI:10.1105/tpc.006676
|
|
| [27] |
Bosch D, Saiardi A. Arginine transcriptional response does not require inositol phosphate synthesis. J Biol Chem, 2012, 287(45): 38347-38355. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M112.384255
|
|
| [28] |
Sang SH, Chen Y, Yang QF, et al. Arabidopsis inositol polyphosphate multikinase delays flowering time through mediating transcriptional activation of FLOWERING LOCUS C. J Exp Bot, 2017, 68(21/22): 5787-5800.
|
|
| [29] |
Wu KQ, Malik K, Tian LN, et al. Functional analysis of a RPD3 histone deacetylase homologue in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Mol Biol, 2000, 44(2): 167-176. DOI:10.1023/A:1006498413543
|
|
| [30] |
Schmid M, Davison TS, Henz SR, et al. A gene expression map of Arabidopsis thaliana development. Nature Genet, 2005, 37(5): 501-506. DOI:10.1038/ng1543
|
|
| [31] |
Tian L, Chen ZJ. Blocking histone deacetylation in Arabidopsis induces pleiotropic effects on plant gene regulation and development. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2001, 98(1): 200-205. DOI:10.1073/pnas.98.1.200
|
|
| [32] |
Tian L, Wang JL, Fong MP, et al. Genetic control of developmental changes induced by disruption of Arabidopsis histone deacetylase 1 (AtHD1) expression. Genetics, 2003, 165(1): 399-409. DOI:10.1093/genetics/165.1.399
|
|
| [33] |
Krogan NT, Hogan K, Long JA. APETALA2 negatively regulates multiple floral organ identity genes in Arabidopsis by recruiting the co-repressor TOPLESS and the histone deacetylase HDA19. Development, 2012, 139(22): 4180-4190. DOI:10.1242/dev.085407
|
|
| [34] |
Perrella G, Lopez-Vernaza MA, Carr C, et al. Histone deacetylase complex1 expression level titrates plant growth and abscisic acid sensitivity in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell, 2013, 25(9): 3491-3505. DOI:10.1105/tpc.113.114835
|
|
| [35] |
Wang Z, Cao H, Sun YZ, et al. Arabidopsis paired amphipathic helix proteins SNL1 and SNL2 redundantly regulate primary seed dormancy via abscisic acid-ethylene antagonism mediated by histone deacetylation. Plant Cell, 2013, 25(1): 149-166. DOI:10.1105/tpc.112.108191
|
|
| [36] |
Ning YQ, Chen Q, Lin RN, et al. The HDA19 histone deacetylase complex is involved in the regulation of flowering time in a photoperiod-dependent manner. Plant J, 2019, 98(3): 448-464. DOI:10.1111/tpj.14229
|
|
| [37] |
Kim W, Latrasse D, Servet C, et al. Arabidopsis histone deacetylase HDA9 regulates flowering time through repression of AGL19. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2013, 432(2): 394-398. DOI:10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.11.102
|
|
| [38] |
Kang MJ, Jin HS, Noh YS, et al. Repression of flowering under a noninductive photoperiod by the HDA9-AGL19-FT module in Arabidopsis. New Phytol, 2015, 206(1): 281-294. DOI:10.1111/nph.13161
|
|
| [39] |
Schönrock N, Bouveret R, Leroy O, et al. Polycomb-group proteins repress the floral activator AGL19 in the FLC-independent vernalization pathway. Genes Dev, 2006, 20(12): 1667-1678. DOI:10.1101/gad.377206
|
|
| [40] |
Park HJ, Baek D, Cha JY, et al. HOS15 interacts with the histone deacetylase HDA9 and the evening complex to epigenetically regulate the floral activator GIGANTEA. Plant Cell, 2019, 31(1): 37-51. DOI:10.1105/tpc.18.00721
|
|
| [41] |
Zhu JH, Jeong JC, Zhu YM, et al. Involvement of Arabidopsis HOS15 in histone deacetylation and cold tolerance. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2008, 105(12): 4945-4950. DOI:10.1073/pnas.0801029105
|
|
| [42] |
Kim YJ, Wang RZ, Gao L, et al. POWERDRESS and HDA9 interact and promote histone H3 deacetylation at specific genomic sites in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2016, 113(51): 14858-14863. DOI:10.1073/pnas.1618618114
|
|
| [43] |
Merini W, Calonje M. PRC1 is taking the lead in PcG repression. Plant J, 2015, 83(1): 110-120. DOI:10.1111/tpj.12818
|
|
| [44] |
Wang QN, Shen WH. Chromatin modulation and gene regulation in plants: insight about PRC1 function. Biochem Soc Trans, 2018, 46(4): 957-966. DOI:10.1042/BST20170576
|
|
| [45] |
Förderer A, Zhou Y, Turck F. The age of multiplexity: recruitment and interactions of polycomb complexes in plants. Curr Opin Plant Biol, 2016, 29: 169-178. DOI:10.1016/j.pbi.2015.11.010
|
|
| [46] | |
|
| [47] |
Chanvivattana Y, Bishopp A, Schubert D, et al. Interaction of polycomb-group proteins controlling flowering in Arabidopsis. Development, 2004, 131(21): 5263-5276. DOI:10.1242/dev.01400
|
|
| [48] |
Zeng XL, Gao Z, Jiang C, et al. HISTONE DEACETYLASE 9 functions with polycomb silencing to repress FLOWERING LOCUS C expression. Plant Physiol, 2020, 182(1): 555-565. DOI:10.1104/pp.19.00793
|
|
| [49] |
Jiang W, Wei DY, Zhou WW, et al. HDA9 interacts with the promoters of SOC1 and AGL24 involved in flowering time control in Brassica juncea. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2018, 499(3): 519-523. DOI:10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.03.180
|
|
| [50] |
张俊利, 蒋炜, 李晟男, 等. 芥菜HDA9突变体构建及其与开花整合子 SOC1、 AGL24启动子互作. 生物工程学报, 2020, 36(6): 1170-1180. Zhang JL, Jiang W, Li SN, et al. Mutant construction of HDA9 and its interactions with promoters of flowering integrator SOC1 and AGL24 in Brassica juncea. Chin J Biotech, 2020, 36(6): 1170-1180 (in Chinese).
|
|
| [51] | |
|
| [52] |
Zheng Y, Ding Y, Sun X, et al. Histone deacetylase HDA9 negatively regulates salt and drought stress responsiveness in Arabidopsis. J Exp Bot, 2016, 67(6): 1703-1713. DOI:10.1093/jxb/erv562
|
|
| [53] |
Baek D, Shin G, Kim MC, et al. Histone deacetylase HDA9 with ABI4 contributes to abscisic acid homeostasis in drought stress response. Front Plant Sci, 2020, 11: 143. DOI:10.3389/fpls.2020.00143
|
|
| [54] |
Khan IU, Ali A, Khan HA, et al. PWR/HDA9/ABI4 complex epigenetically regulates ABA dependent drought stress tolerance in Arabidopsis. Front Plant Sci, 2020, 11: 623. DOI:10.3389/fpls.2020.00623
|
|
| [55] |
Zheng Y, Ge JY, Bao C, et al. Histone deacetylase HDA9 and WRKY53 transcription factor are mutual antagonists in regulation of plant stress response. Mol Plant, 2020, 13(4): 598-611. DOI:10.1016/j.molp.2019.12.011
|
|
| [56] |
Shen Y, Lei TT, Cui XY, et al. Arabidopsis histone deacetylase HDA15 directly represses plant response to elevated ambient temperature. Plant J, 2019, 100(5): 991-1006. DOI:10.1111/tpj.14492
|
|
| [57] |
Liu XC, Chen CY, Wang KC, et al. PHYTOCHROME INTERACTING FACTOR 3 associates with the histone deacetylase HDA15 in repression of chlorophyll biosynthesis and photosynthesis in etiolated Arabidopsis seedlings. Plant Cell, 2013, 25(4): 1258-1273. DOI:10.1105/tpc.113.109710
|
|
| [58] |
Benhamed M, Bertrand C, Servet C, et al. Arabidopsis GCN5, HD1, and TAF1/HAF2 interact to regulate histone acetylation required for light-responsive gene expression. Plant Cell, 2006, 18(11): 2893-2903. DOI:10.1105/tpc.106.043489
|
|
| [59] | |
|
| [60] |
Zhao LM, Peng T, Chen CY, et al. HY5 interacts with the histone deacetylase HDA15 to repress hypocotyl cell elongation in photomorphogenesis. Plant Physiol, 2019, 180(3): 1450-1466. DOI:10.1104/pp.19.00055
|
|
| [61] |
Tang Y, Liu XC, Liu X, et al. Arabidopsis NF-YCs mediate the light-controlled hypocotyl elongation via modulating histone acetylation. Mol Plant, 2017, 10(2): 260-273. DOI:10.1016/j.molp.2016.11.007
|
|
| [62] |
van der Woude LC, Perrella G, Snoek BL, et al. HISTONE DEACETYLASE 9 stimulates auxin-dependent thermomorphogenesis in Arabidopsis thaliana by mediating H2A.Z depletion. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2019, 116(50): 25343-25354. DOI:10.1073/pnas.1911694116
|
|
| [63] |
Yang LY, Chen XS, Wang ZX, et al. HOS15 and HDA9 negatively regulate immunity through histone deacetylation of intracellular immune receptor NLR genes in Arabidopsis. New Phytol, 2020, 226(2): 507-522. DOI:10.1111/nph.16380
|
|
| [64] |
Wang YZ, Hu Q, Wu ZJ, et al. HISTONE DEACETYLASE 6 represses pathogen defence responses in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Environ, 2017, 40(12): 2972-2986. DOI:10.1111/pce.13047
|
|
| [65] |
Devoto A, Nieto-Rostro M, Xie DX, et al. COI 1 links jasmonate signalling and fertility to the SCF ubiquitin-ligase complex in Arabidopsis. Plant J, 2002, 32(4): 457-466. DOI:10.1046/j.1365-313X.2002.01432.x
|
|
| [66] |
Zhou CH, Zhang L, Duan J, et al. HISTONE DEACETYLASE 19 is involved in jasmonic acid and ethylene signaling of pathogen response in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell, 2005, 17(4): 1196-1204. DOI:10.1105/tpc.104.028514
|
|
| [67] |
Song CP, Agarwal M, Ohta M, et al. Role of an Arabidopsis AP2/EREBP-type transcriptional repressor in abscisic acid and drought stress responses. Plant Cell, 2005, 17(8): 2384-2396. DOI:10.1105/tpc.105.033043
|
|
| [68] |
Lee HG, Seo PJ. MYB96 recruits the HDA15 protein to suppress negative regulators of ABA signaling in Arabidopsis. Nat Commun, 2019, 10: 1713. DOI:10.1038/s41467-019-09417-1
|
|
| [69] |
Hao YH, Wang HJ, Qiao SL, et al. Histone deacetylase HDA6 enhances brassinosteroid signaling by inhibiting the BIN2 kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2016, 113(37): 10418-10423. DOI:10.1073/pnas.1521363113
|
|
| [70] |
Kim H, Shim D, Moon S, et al. Transcriptional network regulation of the brassinosteroid signaling pathway by the BES1-TPL-HDA19 co-repressor complex. Planta, 2019, 250(4): 1371-1377. DOI:10.1007/s00425-019-03233-z
|
|
| [71] |
Yuan LB, Chen X, Chen HH, et al. Histone deacetylases HDA6 and HDA9 coordinately regulate valve cell elongation through affecting auxin signaling in Arabidopsis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2019, 508(3): 695-700. DOI:10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.11.082
|
|
| [72] |
Zhou Y, Tan B, Luo M, et al. HISTONE DEACETYLASE 19 interacts with HSL1 and participates in the repression of seed maturation genes in Arabidopsis seedlings. Plant Cell, 2013, 25(1): 134-148. DOI:10.1105/tpc.112.096313
|
|
| [73] |
Chhun T, Chong SY, Park BS, et al. HSI2 repressor recruits MED13 and HDA6 to down-regulate seed maturation gene expression directly during Arabidopsis early seedling growth. Plant Cell Physiol, 2016, 57(8): 1689-1706. DOI:10.1093/pcp/pcw095
|
|
| [74] |
Van Zanten M, Zoll C, Wang Z, et al. HISTONE DEACETYLASE 9 represses seedling traits in Arabidopsis thaliana dry seeds. Plant J, 2014, 80(3): 475-488. DOI:10.1111/tpj.12646
|
|
| [75] |
Gu DC, Chen CY, Zhao ML, et al. Identification of HDA15-PIF1 as a key repression module directing the transcriptional network of seed germination in the dark. Nucleic Acids Res, 2017, 45(12): 7137-7150. DOI:10.1093/nar/gkx283
|
|
| [76] |
Lee K, Park OS, Jung SJ, et al. Histone deacetylation-mediated cellular dedifferentiation in Arabidopsis. J Plant Physiol, 2016, 191: 95-100. DOI:10.1016/j.jplph.2015.12.006
|
|
| [77] |
Chen XS, Lu L, Mayer KS, et al. POWERDRESS interacts with HISTONE DEACETYLASE 9 to promote aging in Arabidopsis. eLife, 2016, 5: e17214. DOI:10.7554/eLife.17214
|
|
| [78] | |
|
| [79] |
Wang L, Kim J, Somers DE. Transcriptional corepressor TOPLESS complexes with pseudoresponse regulator proteins and histone deacetylases to regulate circadian transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2013, 110(2): 761-766. DOI:10.1073/pnas.1215010110
|
|
| [80] |
Lee K, Mas P, Seo PJ. The EC-HDA9 complex rhythmically regulates histone acetylation at the TOC1 promoter in Arabidopsis. Commun Biol, 2019, 2: 143. DOI:10.1038/s42003-019-0377-7
|
|
| [81] |
Ueda M, Seki M. Histone modifications form epigenetic regulatory networks to regulate abiotic stress response. Plant Physiol, 2020, 182(1): 15-26. DOI:10.1104/pp.19.00988
|
|
| [82] |
Joshi P, Greco TM, Guise AJ, et al. The functional interactome landscape of the human histone deacetylase family. Mol Syst Biol, 2013, 9: 672. DOI:10.1038/msb.2013.26
|
|
| [83] |
Yang XJ, Seto E. Collaborative spirit of histone deacetylases in regulating chromatin structure and gene expression. Curr Opin Genet Dev, 2003, 13(2): 143-153. DOI:10.1016/S0959-437X(03)00015-7
|
|
| [84] |
Yan K, Ran ML, Li SN, et al. The delayed senescence of postharvest buds in salt ions was related to antioxidant activity, HDA9 and CCX1 in broccoli ( Brassica oleracea L. var. Italic Planch.). Food Chem, 2020, 324: 126887. DOI:10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.126887
|
|
| [85] |
Zhou Y, Yang P, Zhang F, et al. Histone deacetylase HDA19 interacts with histone methyltransferase SUVH5 to regulate seed dormancy in Arabidopsis. Plant Biol, 2020. DOI:10.1111/plb.13158
|
|
 2021, Vol. 37
2021, Vol. 37